In few days we shall cover the whole of Gingiva in multiple posts. We shall start with Types of Gingiva in this post.
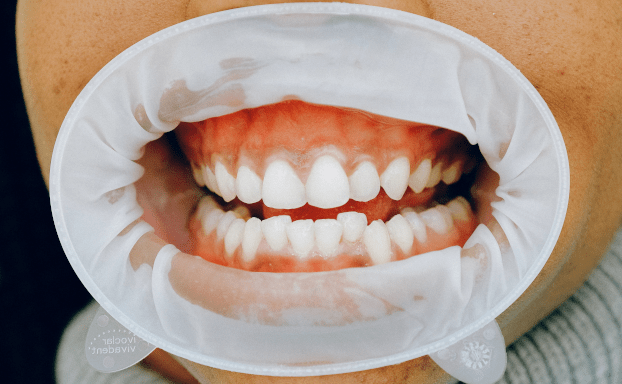
Gingiva is a masticatory mucosa and covers the alveolar process of the jaw and surround the neck of the teeth.
The gingiva extends from the dentogingival junction to the alveolar mucosa. It is subject to friction and pressure of mastication.
The stratified squamous epithelium may be keratinized or non-keratinized but most often it is parakeratinized.
Gingiva appears slightly depressed between adjacent teeth, corresponding the depression on the alveolar process between eminence of the sockets
The gingiva is limited on the outer surface of both the jaws by the mucoginigival junction, which separates it from the alveolar mucosa.
The alveolar mucosa is red & contains numerous small vessels coursing close to the surface.
The gingiva is normal pink but sometimes have grayish tint.
Gingiva is attached immovably and firmly to the periosteum of the alveolar bone.
On the inner surface of the lower jaw a line of demarcation is found between the gingiva and the mucosa on the floor of the mouth.
Types of Gingiva
Three different types of Gingiva are:
A. Free/unattached/marginal gingiva
The free gingiva is the terminal edge of the gingiva which is usually about 1mm wide and surround the teeth.
The free gingiva forms one of the walls of the gingival sulcus and is separated from the attached gingiva by a groove called free gingival groove.
B. Inter-dental Papilla
It is the part of gingiva that fills the space between two adjacent teeth.
It is a shallow V shaped space surrounding the tooth.
It is bounded on one side by the tooth and on the other side by the free gingiva
From oral or vestibular aspect, the surface of the inter-dental papilla is triangular.
The depressed part of inter dental papilla is called COL.
Col is covered by thin non-keratinized epithelium.
Elastic fibers known as Oxytalan fibers are present.
C. Attached Gingiva
It is continuation of the free gingiva and extends up to the alveolar mucosa.
The attached gingiva is separated from the alveolar mucosa by a mucogingival sulcus.
The width of attached gingiva is:
In maxillary anterior region: 3.5 – 4.5mm
In mandibular anterior region: 3.3 -3.9mm
Posteriorly, the width of attached gingiva is less
It is the least at first premolar area:
In Maxilla: 1.9 mm
In Mandible: 1.8 mm
This is beginning of the topic of Gingiva. We shall cover the whole topic in the coming days.
Last updated on May 13th, 2020 at 12:11