Before we begin with the details of access opening of Maxillary Central Incisor, lets see a few terminologies.
Pulp Cavity
Present in the tooth, surrounded by dentin except at the apical foramina or the tip of the root. The coronal portion is called pulp chamber and the radicular portion is called root canal.
Pulp Chamber
In single rooted teeth, pulp chamber gradually merge into the root canal.
In multi rooted teeth, the pulp chamber is single with multiple root canals.
Roof of pulp chamber consists of dentin covering occlusally or incisally
Pulp horns is a bump in the roof under the cusp or under developmental lobe.
Floor of pulp runs parallel to the roof.
Canal Orifices are openings in the floor of pulp chamber which leads to root canals.
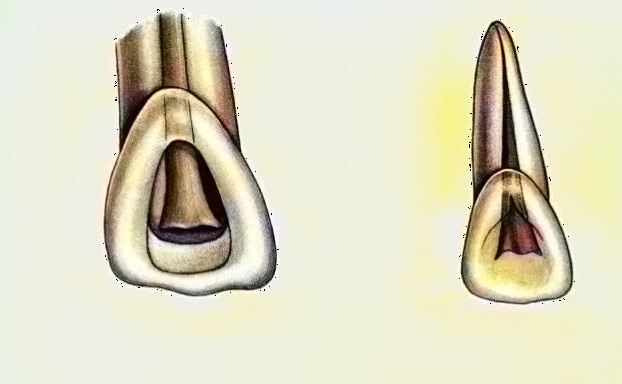
Access opening in Maxillary Central Incisor
Average Length of the tooth: 22.8 mm
Pulp Chamber: Located in the center of the crown and is at equal distance from the neighboring dentinal walls. It is broad mediodistally. Pulp follows the contour of the crown and has 3 pulp horns due to developmental mamelons in young tooth. Chamber is ovoid mesiodistally. Root canal and pulp chamber are continuous with no distinction.
Root And Root Canal:
The maxillary central incisor has one root and one root canal. Root Canal is broad labiopalatally, conical in shape and located at the center. In cross section, the canal is ovoid mesiodistally in cervical third, ovoid to almost round in middle third and round at the apical third.
Access Opening
The shape, size and coronal extension is determined from a diagnostic radiograph.
The enamel is penetrated in the center of the lingual surface at perpendicular angel with a round bur (No. 4).
After enamel is penetrated, bur is directed along the long axis of tooth until pulp chamber is reached and a drop is felt if chamber is large.
Similarly, Overhanging enamel and dentin is removed including pulp horns.
A Gates-Glidden drill of the proper size is used to remove palatal shoulder. Remember the palatal shoulder is not an anatomic landmark but the prominence of dentin created when palatal roof is removed.
After the removal, direct access can be seen to the apical area by removing the palatal roof and palatal shoulder.
Check if direct access has been established by placing the straight end of endodontic explorer into the canal orifice.
Access Opening in Maxillary Central Incisor
We hope that this post will clear some of the doubts of the Access Cavity preparation of Maxillary Central Incisor.